Difference between revisions of "Database Metadata"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | Which will display only results with virtual column "con_name" has the value "Po Ping". Not the $ symbol to refer to a virtual column. | + | Which will display only results with virtual column "con_name" has the value "Po Ping". Not the $ symbol to refer to a virtual column. You can learn more on this in the next section. |
| + | == Database Query syntax == | ||
| + | The syntax used in the Database Query is defined as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | SENTENCE|TABLES|QUERY | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where TABLES is a list of meta-tables separated by a comma. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SELECT|TABLE | ||
| + | SELECT|TABLE|FILTER | ||
| + | |||
| + | where TABLE is an unique meta-table. | ||
| + | |||
| + | UPDATE|TABLE | ||
| + | UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES | ||
| + | UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES|FILTER | ||
| + | |||
| + | where TABLE is an unique meta-table. | ||
| + | |||
| + | DELETE|TABLE | ||
| + | DELETE|TABLE|FILTER | ||
| + | |||
| + | where TABLE is an unique meta-table. | ||
[[Category: Extension Guide]] | [[Category: Extension Guide]] | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 19 July 2011
When you creates an extension is very common the need of a database to store data. You can create tables, but also need to create a bean with Hibernate XML mapping or annotations, a DAO, etc. The other way is creating meta-tables. These virtual tables are part of the OpenKM 5.1 Database Metadata feature. Let's see an example.
Our costumer want us to create a contact management. For this, we are going to create the metadata structure:
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col00', 'integer', 'con_id');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col01', 'text', 'con_name');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col02', 'text', 'con_mail');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col03', 'text', 'con_phone');
In this sample, the meta-table "contact" contains 4 columns:
- COL 0 -> con_id
- COL 1 -> con_name
- COL 2 -> con_mail
- COL 3 -> con_phone
| Actually a meta-table can contain no more than 15 columns. |
An if you go to Administration -> Database Query you can see this new empty table:
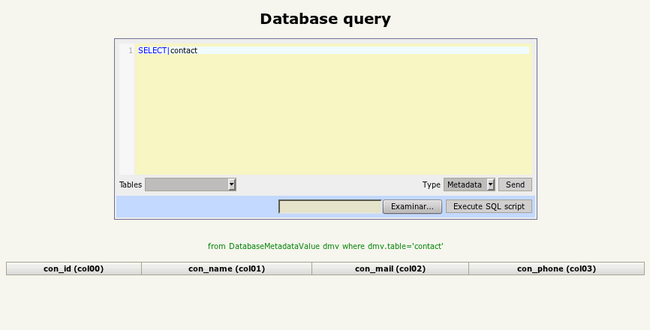
Let's insert some data:
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '1', 'Tai Lung', 'tlung@openkm.com', '555112233');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '2', 'Po Ping', 'pping@openkm.com', '555223344');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '3', 'Master Shifu', 'mshifu@openkm.com', '555334455');
This is the executed query again:
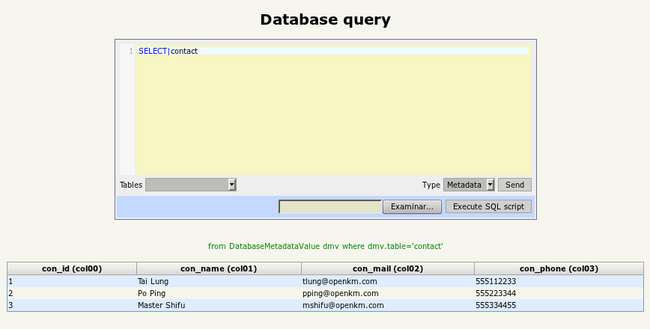
As you can see, now the inserted data is shown under its correct column. But this is not all, you can also filter these results using this syntax:
SELECT|contact|$con_name='Po Ping'
Which will display only results with virtual column "con_name" has the value "Po Ping". Not the $ symbol to refer to a virtual column. You can learn more on this in the next section.
Database Query syntax
The syntax used in the Database Query is defined as:
SENTENCE|TABLES|QUERY
Where TABLES is a list of meta-tables separated by a comma.
SELECT|TABLE SELECT|TABLE|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.
UPDATE|TABLE UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.
DELETE|TABLE DELETE|TABLE|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.