Difference between revisions of "Use of node node"
From OpenKM Documentation
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last line of this action tell the jBPM engine to go to the next node, which in this case is the end node. | ||
[[Category: Workflow Guide]] | [[Category: Workflow Guide]] | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 13 January 2012
You can define the behavior of a node of type node suing the Action element. This Action is executed when the process arrives to the node.
The Action to be executed can be defined in two ways:
- Using a BeanShell script.
- Using an action handler, this is a Java class which implements the ActionHandler interface.
Below we are going to create a sample process with a node node which make use of an implementation of the ActionHandler interface.
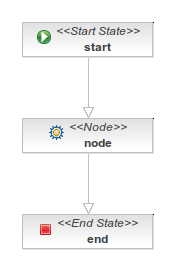
In this image you can see the process definition graph:
This process begins in a start node and go to a node node where the action to be performed is defined by the class MyAction which implements the ActionHandler interface.
public class MyAction implements ActionHandler {
@Override
public void execute(ExecutionContext executionContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Executing programmed action...");
// Go to next node
executionContext.getProcessInstance().signal();
}
}
The last line of this action tell the jBPM engine to go to the next node, which in this case is the end node.