Database Metadata
When you create an extension, the need for a database to store data is very common. You can create tables, but also need to create a bean with Hibernate XML mapping or annotations, a DAO, etc. The other way is creating meta-tables. These virtual tables are part of the OpenKM 5.1 Database Metadata feature. Let's see an example.
Actually there are several data types available:
- text
- boolean
- integer
- long
Our customer wants us to create a contact management feature. For this, we are going to create the metadata structure:
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col00', 'integer', 'con_id');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col01', 'text', 'con_name');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col02', 'text', 'con_mail');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_TYPE (DMT_TABLE, DMT_REAL_COLUMN, DMT_TYPE, DMT_VIRTUAL_COLUMN) VALUES ('contact', 'col03', 'text', 'con_phone');
In this sample, the meta-table "contact" contains 4 columns:
- COL 0 -> con_id
- COL 1 -> con_name
- COL 2 -> con_mail
- COL 3 -> con_phone
| Actually a meta-table can contain no more than 15 columns. |
And if you go to Administration -> Database Query you can see this new empty table:
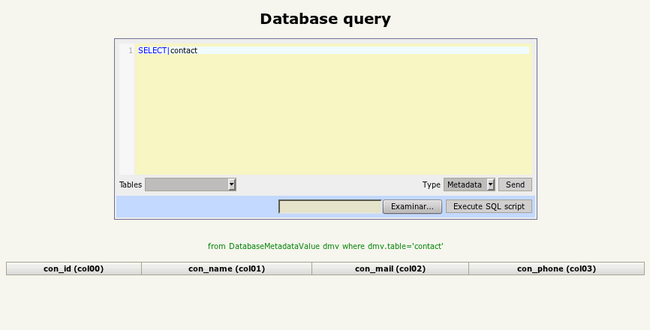
Let's insert some data:
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '1', 'Tai Lung', 'tlung@openkm.com', '555112233');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '2', 'Po Ping', 'pping@openkm.com', '555223344');
INSERT INTO OKM_DB_METADATA_VALUE (DMV_TABLE, DMV_COL00, DMV_COL01, DMV_COL02, DMV_COL03) VALUES ('contact', '3', 'Master Shifu', 'mshifu@openkm.com', '555334455');
This is the executed query again:
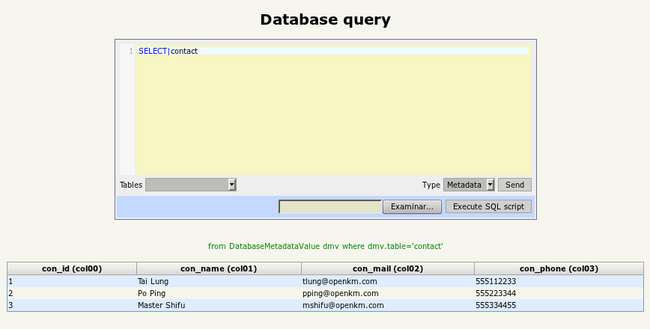
As you can see, now the inserted data is shown under its correct column. But this is not all, you can also filter these results using this syntax:
SELECT|contact|$con_name='Po Ping'
Which will display only results with virtual column "con_name" has the value "Po Ping". Not the $ symbol to refer to a virtual column. You can learn more on this in the next section.
Database Query syntax
The syntax used in the Database Query is defined as:
SENTENCE|TABLES|QUERY
Where TABLES is a list of meta-tables separated by a comma.
SELECT|TABLE SELECT|TABLE|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.
UPDATE|TABLE UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES UPDATE|TABLE|VALUES|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.
DELETE|TABLE DELETE|TABLE|FILTER
where TABLE is an unique meta-table.
This is a sample JOIN query using metadata sintax:
SENTENCE|expediente,municipio|from DatabaseMetadataValue expe, DatabaseMetadataValue mun
where expe.table='expediente' and mun.table='municipio' and expe.$exp_mun_id=mun.$mun_id
Use from Java
Obviously Database metadata can also be used from Java. This way you can implement your own extensions which make use of this feature. This can be achieved by making use of these static methods:
String DatabaseMetadataUtils.buildQuery(String table, String filter, String order)
String DatabaseMetadataUtils.buildUpdate(String table, String values, String filter)
String DatabaseMetadataUtils.buildDelete(String table, String filter)
Each one of these methods will return a Hibernate query with the $xxx columns already replaced by its real-column counterpart. And this Hibernate query can be executed, for example. by:
List<Object> LegacyDAO.executeQuery(String query)
The returned list, in this case, will be a list of DatabaseMetadataValue objects.
Use from Java (GWT-frontend)
The class OKMDatabaseMetadataService has the interface definition to accessing metadata services.
Class Security
public class GWTExtendedSecurity extends DatabaseMetadataCommon implements IsSerializable {
public static final String TYPE_USER = "user";
public static final String TYPE_ROLE = "role";
// Metadata Virtual Name mapping
public static final String MV_TABLE_NAME = "security";
public static final String MV_COLUMN_NAME_UUID = "uuid_id";
public static final String MV_COLUMN_NAME_TYPE = "type";
public static final String MV_COLUMN_NAME_NAME = "name";
private String uuid;
private String type;
private String name;
@Override
public void loadFromMap(Map<String, String> map) {
super.loadFromMap(map);
if (map.containsKey(MV_COLUMN_NAME_UUID)) {
setUuid(map.get(MV_COLUMN_NAME_UUID));
}
if (map.containsKey(MV_COLUMN_NAME_TYPE)) {
setType(map.get(MV_COLUMN_NAME_TYPE));
}
if (map.containsKey(MV_COLUMN_NAME_NAME)) {
setName(map.get(MV_COLUMN_NAME_NAME));
}
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> restoreToMap() {
Map<String,String> map = super.restoreToMap();
if (uuid != null) {
map.put(MV_COLUMN_NAME_UUID, getUuid());
}
if (type != null) {
map.put(MV_COLUMN_NAME_TYPE, getType());
}
if (name != null) {
map.put(MV_COLUMN_NAME_NAME, getName());
}
return map;
}
public String getUuid() {
return uuid;
}
public void setUuid(String uuid) {
this.uuid = uuid;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Class example
public class Example {
private final OKMDatabaseMetadataServiceAsync metadataService = (OKMDatabaseMetadataServiceAsync) GWT.create(OKMDatabaseMetadataService.class);
public test() {
// get sequence
metadataService.getNextSequenceValue("table_name", "col_name" , new AsyncCallback<Double>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Double result) {
int value = result.intValue();
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
}
});
// create value
final GWTExtendedSecurity security = new GWTExtendedSecurity();
security.setUuid("some uuid");
security.setName("some name");
security.setType(GWTExtendedSecurity.TYPE_ROLE);
security.setRealTable(GWTExtendedSecurity.MV_TABLE_NAME);
Homex.get().status.setAddGrant();
metadataService.createValue(security.restoreToMap(), new AsyncCallback<Double>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Double result) {
// created
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
}
});
}
Sequences
To work with sequences there's the class getNextSequenceValue(String table, String column). Table indicates metadata table name and column indicates some metadata column name.
Sequences are stored int OKM_DB_METADATA_SEQUENCE table. Any new sequence start by default with value 1. When getNextSequenceValue method is executed if sequence not exists is automatically created.
/**
* getNewContactID
*/
public static long getNewContactID() throws DatabaseException {
return DatabaseMetadataDAO.getNextSequenceValue("contact", con_id);
}